精尽 MyBatis 源码分析 —— 反射模块
1. 概述
本文,我们来分享 MyBatis 的反射模块,对应 reflection 包。如下图所示:
reflection 包
- 相比
parsing包来说,reflection包的代码量大概是 2-3 倍。当然,不要慌,都是比较简单的代码。 - 当然,这是一篇非常非常非常长的博客,因为笔者基本贴了这个模块所有的代码。如果想要比较好的理解这个模块,胖友一定要基于 MyBatis 提供的这个模块的单元测试,多多调试。
在 《精尽 MyBatis 源码解析 —— 项目结构一览》 中,简单介绍了这个模块如下:
Java 中的反射虽然功能强大,但对大多数开发人员来说,写出高质量的反射代码还是 有一定难度的。MyBatis 中专门提供了反射模块,该模块对 Java 原生的反射进行了良好的封装,提了更加简洁易用的 API,方便上层使调用,并且对反射操作进行了一系列优化,例如缓存了类的元数据,提高了反射操作的性能。
下面,我们就来看看具体的源码。因为 reflection 是基础支持层,所以建议胖友在我们讲解到的类和方法中,打折断点一起来了解。
2. Reflector
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector ,反射器,每个 Reflector 对应一个类。Reflector 会缓存反射操作需要的类的信息,例如:构造方法、属性名、setting / getting 方法等等。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
type属性,每个 Reflector 对应的类。defaultConstructor属性,默认无参构造方法。在<1>处初始化,详细解析,见 「2.1 addDefaultConstructor」 。getMethods、getTypes属性,分别为属性对应的 getting 方法、getting 方法的返回类型的映射。在<2>处初始化,详细解析,见 「2.2 addGetMethods」 。setMethods、setTypes属性,分别为属性对应的 setting 方法、setting 方法的参数类型的映射。在<3>处初始化,详细解析,见 「2.3 addSetMethods」 。<4>处,根据初始化的getMethods+getTypes和setMethods+setTypes,通过遍历获取 fields 属性。详细解析,见 「2.4 addFields」 。<5>处,初始化readablePropertyNames、writeablePropertyNames、caseInsensitivePropertyMap属性。
2.1 addDefaultConstructor
#addDefaultConstructor(Class<?> clazz) 方法,查找默认无参构造方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
2.2 addGetMethods
#addGetMethods(Class<?> cls) 方法,初始化 getMethods 和 getTypes ,通过遍历 getting 方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
<1>处,conflictingGetters变量,属性与其 getting 方法的映射。因为父类和子类都可能定义了相同属性的 getting 方法,所以VALUE会是个数组。<2>处,遍历所有方法,挑选符合的 getting 方法,添加到conflictingGetters中。<2.1>处,方法参数大于 0 ,说明不是 getting 方法,忽略。<2.2>处,过滤 getting 方法, 以 get 和 is 方法名开头。<2.3>处,调用#addMethodConflict(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingMethods, String name, Method method)方法,添加到conflictingGetters中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6// Reflector.java
private void addMethodConflict(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingMethods, String name, Method method) {
List<Method> list = conflictingMethods.computeIfAbsent(name, k -> new ArrayList<>());
list.add(method);
}- JDK8 编写这样的逻辑,真心方便。
<3>处,调用#resolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>>)方法,解决 getting 冲突方法。详细解析,见 「2.2.2 resolveGetterConflicts」 。
2.2.1 getClassMethods
#getClassMethods(Class<?> cls) 方法,获得所有方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
代码比较简单,胖友自己看注释。
<1>和<2>处,会调用#addUniqueMethods(Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods, Method[] methods)方法,添加方法数组到uniqueMethods中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18// Reflector.java
private void addUniqueMethods(Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods, Method[] methods) {
for (Method currentMethod : methods) {
if (!currentMethod.isBridge()) {
// <3> 获得方法签名
String signature = getSignature(currentMethod);
// check to see if the method is already known
// if it is known, then an extended class must have
// overridden a method
// 当 uniqueMethods 不存在时,进行添加,最终只会存在末级子类的方法
if (!uniqueMethods.containsKey(signature)) {
// 添加到 uniqueMethods 中
uniqueMethods.put(signature, currentMethod);
}
}
}
}<3>处,会调用#getSignature(Method method)方法,获得方法签名。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23// Reflector.java
private String getSignature(Method method) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 返回类型
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (returnType != null) {
sb.append(returnType.getName()).append('#');
}
// 方法名
sb.append(method.getName());
// 方法参数
Class<?>[] parameters = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
sb.append(':');
} else {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(parameters[i].getName());
}
return sb.toString();
}- 格式:
returnType#方法名:参数名1,参数名2,参数名3。 - 例如:
void#checkPackageAccess:java.lang.ClassLoader,boolean。
- 格式:
2.2.2 resolveGetterConflicts
#resolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>>) 方法,解决 getting 冲突方法。最终,一个属性,只保留一个对应的方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
总体比较简单,胖友自己瞅瞅。我们只说两个关键点哈。
<1>处,基于返回类型比较。重点在<1.1>和<1.2>的情况,因为子类可以修改放大返回值,所以在出现这个情况时,选择子类的该方法。例如,父类的一个方法的返回值为 List ,子类对该方法的返回值可以覆写为 ArrayList 。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class A {
List<String> getXXXX();
}
public class B extends A {
ArrayList<String> getXXXX(); // 选择它
}<2>处,调用#addGetMethod(String name, Method method)方法,添加方法到getMethods和getTypes中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// Reflector.java
private void addGetMethod(String name, Method method, boolean isAmbiguous) {
// <2.1> 判断是查找到最匹配的方法。
MethodInvoker invoker = isAmbiguous ? new AmbiguousMethodInvoker(method, MessageFormat.format(
"Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property ''{0}'' in class ''{1}''. This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results.",
name, method.getDeclaringClass().getName())) : new MethodInvoker(method);
// <2.2> 添加到 getMethods 中
getMethods.put(name, invoker);
// <2.3> 添加到 getTypes 中
Type returnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, type);
getTypes.put(name, typeToClass(returnType));
}<2.1>处,判断是查找到最匹配的方法。代码如下:<2.2>处,添加到getMethods中。此处,我们可以看到一个 MethodInvoker 类,详细解析,见 「4.3 MethodInvoker」 。<2.3>处,添加到getTypes中。此处,我们可以看到一个 TypeParameterResolver 类,详细解析,见 「14. TypeParameterResolver」 。
#typeToClass(Type src)方法,获得java.lang.reflect.Type对应的类。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26// Reflector.java
private Class<?> typeToClass(Type src) {
Class<?> result = null;
// 普通类型,直接使用类
if (src instanceof Class) {
result = (Class<?>) src;
// 泛型类型,使用泛型
} else if (src instanceof ParameterizedType) {
result = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) src).getRawType();
// 泛型数组,获得具体类
} else if (src instanceof GenericArrayType) {
Type componentType = ((GenericArrayType) src).getGenericComponentType();
if (componentType instanceof Class) { // 普通类型
result = Array.newInstance((Class<?>) componentType, 0).getClass();
} else {
Class<?> componentClass = typeToClass(componentType); // 递归该方法,返回类
result = Array.newInstance(componentClass, 0).getClass();
}
}
// 都不符合,使用 Object 类
if (result == null) {
result = Object.class;
}
return result;
}- 代码比较简单,就是寻找 Type 真正对应的类。
2.3 addSetMethods
#addSetMethods(Class<?> cls) 方法,初始化 setMethods 和 setTypes ,通过遍历 setting 方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
- 总体逻辑和
#addGetMethods(Class<?> cls)方法差不多。主要差异点在<1>和<2>处。因为<1>一眼就能明白,所以我们只看<2>,调用#resolveSetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingSetters)方法,解决 setting 冲突方法。详细解析,见 「2.3.1 resolveSetterConflicts」 中。
2.3.1 resolveSetterConflicts
#resolveSetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingSetters) 方法,解决 setting 冲突方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
总体比较简单,胖友自己瞅瞅。我们只说两个关键点哈。
<1>处,解决冲突 setting 方法的方式,实际和 getting 方法的方式是不太一样的。首先,多的就是考虑了对应的getterType为优先级最高。其次,#pickBetterSetter(Method setter1, Method setter2, String property)方法,选择一个更加匹配的,和 getting 方法是相同的,因为要选择精准的方法。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17// Reflector.java
private Method pickBetterSetter(Method setter1, Method setter2, String property) {
if (setter1 == null) {
return setter2;
}
Class<?> paramType1 = setter1.getParameterTypes()[0];
Class<?> paramType2 = setter2.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (paramType1.isAssignableFrom(paramType2)) {
return setter2;
} else if (paramType2.isAssignableFrom(paramType1)) {
return setter1;
}
throw new ReflectionException("Ambiguous setters defined for property '" + property + "' in class '"
+ setter2.getDeclaringClass() + "' with types '" + paramType1.getName() + "' and '"
+ paramType2.getName() + "'.");
}- 胖友在体会体会。感谢【闷油壶】同学指出问题。
<2>处,调用#addSetMethod(String name, Method method)方法,添加到setMethods和setTypes中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// Reflector.java
private void addSetMethod(String name, Method method) {
if (isValidPropertyName(name)) {
// 添加到 setMethods 中
setMethods.put(name, new MethodInvoker(method));
// 添加到 setTypes 中
Type[] paramTypes = TypeParameterResolver.resolveParamTypes(method, type);
setTypes.put(name, typeToClass(paramTypes[0]));
}
}- 比较简单,和
#addGetMethod(String name, Method method)方法是类似的。
- 比较简单,和
2.4 addFields
#addFields(Class<?> clazz) 方法,初始化 getMethods + getTypes 和 setMethods + setTypes ,通过遍历 fields 属性。实际上,它是 #addGetMethods(...) 和 #addSetMethods(...) 方法的补充,因为有些 field ,不存在对应的 setting 或 getting 方法,所以直接使用对应的 field ,而不是方法。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
<1>处,若setMethods不存在,则调用#addSetField(Field field)方法,添加到setMethods和setTypes中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// Reflector.java
private void addSetField(Field field) {
// 判断是合理的属性
if (isValidPropertyName(field.getName())) {
// 添加到 setMethods 中
setMethods.put(field.getName(), new SetFieldInvoker(field));
// 添加到 setTypes 中
Type fieldType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveFieldType(field, type);
setTypes.put(field.getName(), typeToClass(fieldType));
}
}- 注意,此处创建的是 SetFieldInvoker 对象。详细解析,见 「4.2 SetFieldInvoker」 。
<2>处,若getMethods不存在,则调用#addGetField(Field field)方法,添加到getMethods和getTypes中。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// Reflector.java
private void addGetField(Field field) {
// 判断是合理的属性
if (isValidPropertyName(field.getName())) {
// 添加到 getMethods 中
getMethods.put(field.getName(), new GetFieldInvoker(field));
// 添加到 getMethods 中
Type fieldType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveFieldType(field, type);
getTypes.put(field.getName(), typeToClass(fieldType));
}
}- 注意,此处创建的是 GetFieldInvoker 对象。详细解析,,见 「4.1 GetFieldInvoker」 。
2.5 其它方法
Reflector 中,还有其它方法,用于对它的属性进行访问。比较简单,感兴趣的胖友,自己来瞅瞅。例如:
1 | // Reflector.java |
3. ReflectorFactory
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectorFactory ,Reflector 工厂接口,用于创建和缓存 Reflector 对象。代码如下:
1 | // ReflectorFactory.java |
3.1 DefaultReflectorFactory
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.DefaultReflectorFactory ,实现 ReflectorFactory 接口,默认的 ReflectorFactory 实现类。代码如下:
1 | // DefaultReflectorFactory.java |
- 代码比较简单,胖友一眼就能看懂。
4. Invoker
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.invoker.Invoker ,调用者接口。代码如下:
1 | // Invoker.java |
- 核心是
#invoke(Object target, Object[] args)方法,执行一次调用。而具体调用什么方法,由子类来实现。
4.1 GetFieldInvoker
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.invoker.GetFieldInvoker ,实现 Invoker 接口,获得 Field 调用者。代码如下:
1 | // GetFieldInvoker.java |
4.2 SetFieldInvoker
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.invoker.SetFieldInvoker ,实现 Invoker 接口,设置 Field 调用者。代码如下:
1 | // SetFieldInvoker.java |
4.3 MethodInvoker
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.invoker.MethodInvoker ,实现 Invoker 接口,指定方法的调用器。代码如下:
1 | // MethodInvoker.java |
5. ObjectFactory
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.factory.ObjectFactory ,Object 工厂接口,用于创建指定类的对象。代码如下:
1 | // ObjectFactory.java |
- 比较简单,一共有三类方法。
5.1 DefaultObjectFactory
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.factory.DefaultObjectFactory ,实现 ObjectFactory、Serializable 接口,默认 ObjectFactory 实现类。
5.1.1 create
#create(Class<T> type, ...) 方法,创建指定类的对象。代码如下:
1 | // DefaultObjectFactory.java |
<1>处,调用#resolveInterface(Class<?> type)方法,获得需要创建的类。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17// DefaultObjectFactory.java
protected Class<?> resolveInterface(Class<?> type) {
Class<?> classToCreate;
if (type == List.class || type == Collection.class || type == Iterable.class) {
classToCreate = ArrayList.class;
} else if (type == Map.class) {
classToCreate = HashMap.class;
} else if (type == SortedSet.class) { // issue #510 Collections Support
classToCreate = TreeSet.class;
} else if (type == Set.class) {
classToCreate = HashSet.class;
} else {
classToCreate = type;
}
return classToCreate;
}- 对于我们常用的集合接口,返回对应的实现类。
<2>处,调用#instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs)方法,创建指定类的对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41// DefaultObjectFactory.java
private <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs) {
try {
Constructor<T> constructor;
// <x1> 通过无参构造方法,创建指定类的对象
if (constructorArgTypes == null || constructorArgs == null) {
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor();
try {
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance();
}
throw e;
}
}
// <x2> 使用特定构造方法,创建指定类的对象
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor(constructorArgTypes.toArray(new Class[0]));
try {
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[0]));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
throw e;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 拼接 argTypes
String argTypes = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgTypes).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList).stream()
.map(Class::getSimpleName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
// 拼接 argValues
String argValues = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgs).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList).stream()
.map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
// 抛出 ReflectionException 异常
throw new ReflectionException("Error instantiating " + type + " with invalid types (" + argTypes + ") or values ("
+ argValues + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}- 代码比较简单,分成
<x1>、<x2>两种情况。
- 代码比较简单,分成
5.1.2 isCollection
#isCollection(Class<T> type) 方法,判断指定类是否为集合类。代码如下:
1 | // DefaultObjectFactory.java |
- 判断是否为
java.util.Collection的子类。
5.1.3 setProperties
#setProperties(Properties properties) 方法,设置 Properties 。代码如下:
1 | // DefaultObjectFactory.java |
- 目前是个空实现。所以,暂时可以忽略这个方法。
6. Property 工具类
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property 包下,提供了 PropertyCopier、PropertyNamer、PropertyTokenizer 三个属性相关的工具类。接下来,我们逐小节来解析。
6.1 PropertyCopier
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyCopier ,属性复制器。代码如下:
1 | // PropertyNamer.java |
- 比较简单,胖友一眼看懂。
6.2 PropertyNamer
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyNamer ,属性名相关的工具类方法。代码如下:
1 | public final class PropertyNamer { |
- 比较简单,胖友一眼看懂。
6.3 PropertyTokenizer
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyTokenizer ,实现 Iterator 接口,属性分词器,支持迭代器的访问方式。
举个例子,在访问 "order[0].item[0].name" 时,我们希望拆分成 "order[0]"、"item[0]"、"name" 三段,那么就可以通过 PropertyTokenizer 来实现。
6.3.1 构造方法
1 | // PropertyTokenizer.java |
name属性,当前字符串。children属性,剩余字符串。<1>处,初始化name、children字符串,使用'.'作为分隔。indexedName属性,索引的name属性,因为name如果存在index会被更改。<2>处,记录当前name。- index属性,编号。分成两种情况:
name为数组item[0]时,则index为"0"。name为 Mapmap[key]时,则index为"key"。
<3>处,初始化index,并修改name字符串,使用'['作为分隔符。
6.3.2 next
#next() 方法,迭代获得下一个 PropertyTokenizer 对象。代码如下:
1 | // PropertyTokenizer.java |
- 酱紫,它又会执行「6.3.1 构造方法」 的流程。
6.3.3 hasNext
#hasNext() 方法,判断是否有下一个元素。代码如下:
1 | // PropertyTokenizer.java |
6.3.4 其它方法
PropertyTokenizer 中,还有其它方法,比较简单,感兴趣的胖友,自己来瞅瞅。
7. MetaClass
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaClass ,类的元数据,基于 Reflector 和 PropertyTokenizer ,提供对指定类的各种骚操作。
7.1 构造方法
1 | // MetaClass.java |
- 通过构造方法,我们可以看出,一个 MetaClass 对象,对应一个 Class 对象。
目前有两个方法会涉及到调用该构造方法:
①
#forClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory)静态方法,创建指定类的 MetaClass 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5// MetaClass.java
public static MetaClass forClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
return new MetaClass(type, reflectorFactory);
}②
#metaClassForProperty(String name)方法,创建类的指定属性的类的 MetaClass 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// MetaClass.java
public MetaClass metaClassForProperty(String name) {
// 获得属性的类
Class<?> propType = reflector.getGetterType(name);
// 创建 MetaClass 对象
return MetaClass.forClass(propType, reflectorFactory);
}
7.2 findProperty
#findProperty(String name, boolean useCamelCaseMapping) 方法,根据表达式,获得属性。代码如下:
1 | // MetaClass.java |
useCamelCaseMapping属性,是否要下划线转驼峰 。但是,在<1>处,我们仅仅看到_被替换成了空串。这是为什么呢?继续往下看。<2>处,调用#findProperty(String name)方法,根据表达式,获得属性。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7// MetaClass.java
public String findProperty(String name) {
// <3> 构建属性
StringBuilder prop = buildProperty(name, new StringBuilder());
return prop.length() > 0 ? prop.toString() : null;
}<3>处,调用#buildProperty(String name, StringBuilder builder)方法,构建属性。代码如下:
1 | // MetaClass.java |
- 创建 PropertyTokenizer 对象,对
name进行分词。当有子表达式,继续递归调用#buildProperty(String name, StringBuilder builder)方法,并将结果添加到builder中;否则,结束,直接添加到builder中。- 在两个
<4>处,解决“下划线转驼峰”的关键是,通过Reflector.caseInsensitivePropertyMap属性,忽略大小写。代码如下:
1 | // Reflector.java |
如果胖友,你有点懵逼,可以运行下 MetaClassTest#shouldFindPropertyName() 这个单元测试方法。
7.3 hasGetter
#hasGetter(String name) 方法,判断指定属性是否有 getting 方法。代码如下:
1 | // MetaClass.java |
思路和
#findProperty((String name, ...)方法是一样的,所以胖友自己看下。<1>处,调用#metaClassForProperty(PropertyTokenizer prop)方法,创建 创建 MetaClass 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54// MetaClass.java
private MetaClass metaClassForProperty(PropertyTokenizer prop) {
// 【调用】获得 getting 方法返回的类型
Class<?> propType = getGetterType(prop);
// 创建 MetaClass 对象
return MetaClass.forClass(propType, reflectorFactory);
}
private Class<?> getGetterType(PropertyTokenizer prop) {
// 获得返回类型
Class<?> type = reflector.getGetterType(prop.getName());
// 如果获取数组的某个位置的元素,则获取其泛型。例如说:list[0].field ,那么就会解析 list 是什么类型,这样才好通过该类型,继续获得 field
if (prop.getIndex() != null && Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
// 【调用】获得返回的类型
Type returnType = getGenericGetterType(prop.getName());
// 如果是泛型,进行解析真正的类型
if (returnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) returnType).getActualTypeArguments();
if (actualTypeArguments != null && actualTypeArguments.length == 1) { // 为什么这里判断大小为 1 呢,因为 Collection 是 Collection<T> ,至多一个。
returnType = actualTypeArguments[0];
if (returnType instanceof Class) {
type = (Class<?>) returnType;
} else if (returnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
type = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) returnType).getRawType();
}
}
}
}
return type;
}
private Type getGenericGetterType(String propertyName) {
try {
// 获得 Invoker 对象
Invoker invoker = reflector.getGetInvoker(propertyName);
// 如果 MethodInvoker 对象,则说明是 getting 方法,解析方法返回类型
if (invoker instanceof MethodInvoker) {
Field _method = MethodInvoker.class.getDeclaredField("method");
_method.setAccessible(true);
Method method = (Method) _method.get(invoker);
return TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, reflector.getType());
}
// 如果 GetFieldInvoker 对象,则说明是 field ,直接访问
if (invoker instanceof GetFieldInvoker) {
Field _field = GetFieldInvoker.class.getDeclaredField("field");
_field.setAccessible(true);
Field field = (Field) _field.get(invoker);
return TypeParameterResolver.resolveFieldType(field, reflector.getType());
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException ignored) {
}
return null;
}- 代码比较长,胖友跟着代码注释,运行下。另外,每个上面的方法, 会调用下面的方法,也就说
metaClassForProperty => getGetterType => getGenericGetterType。
- 代码比较长,胖友跟着代码注释,运行下。另外,每个上面的方法, 会调用下面的方法,也就说
另外,#hasSetter(String name) 方法,判断指定属性是否有 setting 方法。逻辑上,和 #hasGetter(String name) 方法类似,胖友可以自己瞅瞅。
7.4 getGetterType
#getGetterType(String name) 方法,获得指定属性的 getting 方法的返回值的类型。代码如下:
1 | // MetaClass.java |
- 和
#hasGetter(String name)方法类似,胖友可以自己瞅瞅。
另外,#getSetterType(String name) 方法,判断指定属性是否有 setting 方法。逻辑上,和 #getGetterType(String name) 方法类似,胖友可以自己瞅瞅。
7.5 其它方法
MetaClass 还有其它方法,比较简单,是基于 Reflector 方法的封装,感兴趣的胖友,可以自己看看。
8. ObjectWrapper
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.wrapper.ObjectWrapper ,对象包装器接口,基于 MetaClass 工具类,定义对指定对象的各种操作。或者可以说,ObjectWrapper 是 MetaClass 的指定类的具象化。代码如下:
1 | // ObjectWrapper.java |
- 从接口中,我们可以看到,主要是对 MetaObject 方法的调用。
ObjectWrapper 的子类实现如下图: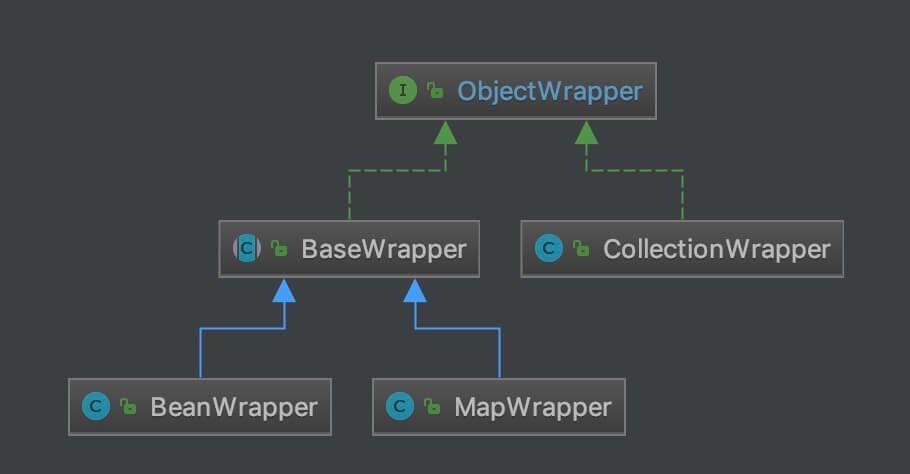 ObjectWrapper 类图
ObjectWrapper 类图
8.1 BaseWrapper
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.wrapper.BaseWrapper ,实现 ObjectWrapper 接口,ObjectWrapper 抽象类,为子类 BeanWrapper 和 MapWrapper 提供属性值的获取和设置的公用方法。代码如下:
1 | // BaseWrapper.java |
- 代码比较简单,胖友看下注释。关于 MetaObject 类,会在 「10. MetaObject」 中,详细解析。
8.1.1 BeanWrapper
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.wrapper.BeanWrapper ,继承 BaseWrapper 抽象类,普通对象的 ObjectWrapper 实现类,例如 User、Order 这样的 POJO 类。属性如下:
1 | // BeanWrapper.java |
8.1.1.1 get
#get(PropertyTokenizer prop) 方法,获得指定属性的值。代码如下:
1 | // BeanWrapper.java |
<1>处,获得集合类型的属性的指定位置的值。例如说:User 对象的list[0]。所调用的方法,都是 BaseWrapper 所提供的公用方法。<2>处,调用#getBeanProperty(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object object)方法,获得属性的值。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// BeanWrapper.java
private Object getBeanProperty(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object object) {
try {
Invoker method = metaClass.getGetInvoker(prop.getName());
try {
return method.invoke(object, NO_ARGUMENTS);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ReflectionException("Could not get property '" + prop.getName() + "' from " + object.getClass() + ". Cause: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}- 通过调用 Invoker 方法,获得属性的值。
8.1.1.2 set
#set(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object value) 方法,设置指定属性的值。代码如下:
1 | // BeanWrapper.java |
- 比较简单,胖友直接看看就成。
8.1.1.3 getGetterType
#getGetterType(String name) 方法,获得指定属性的 getting 方法的返回值。代码如下:
1 | // BeanWrapper.java |
大体逻辑和 MetaClass 的
#getGetterType(String name)方法是一致的。差异点主要在<1>处。<1>metaValue1
2
3
4
5
6
7
处,基于当前属性,创建 MetaObject 对象。如果该属性对应的值为空,那么
SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT1
2
3
4
5
6
7
会等于
metaValue1
2
3
4
5
6
7
。也因为为空,那么就不能基于
@Test public void test01() { RichType object = new RichType(); if (true) { object.setRichType(new RichType()); object.getRichType().setRichMap(new HashMap()); object.getRichType().getRichMap().put("nihao", "123"); } MetaObject meta = MetaObject.forObject(object, SystemMetaObject.DEFAULT_OBJECT_FACTORY, new CustomBeanWrapperFactory(), new DefaultReflectorFactory()); Class<?> clazz = meta.getObjectWrapper().getGetterType("richType.richMap.nihao"); System.out.println(clazz); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
去做递归,获取返回值的类型。
- 关于 MetaObject 类,在 [「10. MetaObject」](http://svip.iocoder.cn/MyBatis/reflection-package/#) 中详细解析。
- 当然,以上说起来比较绕,可以添加如下测试用例,跑一次就大体明白了。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 这个测试用例,就是笔者在代码注释上添加的“例如:`richType.richMap.nihao` ,其中 `richMap` 是 Map 类型,而 `nihao` 的类型,需要获得到 `nihao` 的具体值,才能做真正的判断。”
------
`#getSetterType(String name)` 方法,获得指定属性的 setting 方法的方法参数。逻辑上和 `#getGetterType(String name)` 方法类似的,所以感兴趣的胖友,自己研究。
#### 8.1.1.6 hasGetter
`#hasGetter(String name)` 方法,是否有指定属性的 getting 方法。代码如下:
// BeanWrapper.java
@Override
public boolean hasGetter(String name) {
// 创建 PropertyTokenizer 对象,对 name 进行分词
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
// 有子表达式
if (prop.hasNext()) {
// 判断是否有该属性的 getting 方法
if (metaClass.hasGetter(prop.getIndexedName())) {
// 创建 MetaObject 对象
MetaObject metaValue = metaObject.metaObjectForProperty(prop.getIndexedName());
// 如果 metaValue 为空,则基于 metaClass 判断是否有该属性的 getting 方法
if (metaValue == SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT) {
return metaClass.hasGetter(name);
// 如果 metaValue 非空,则基于 metaValue 判断是否有 getting 方法。
} else {
// 递归判断子表达式 children ,判断是否有 getting 方法
return metaValue.hasGetter(prop.getChildren());
}
} else {
return false;
}
// 有子表达式
} else {
// 判断是否有该属性的 getting 方法
return metaClass.hasGetter(name);
}
}
1 |
|
// BeanWrapper.java
@Override
public MetaObject instantiatePropertyValue(String name, PropertyTokenizer prop, ObjectFactory objectFactory) {
MetaObject metaValue;
// 获得 setting 方法的方法参数类型
Class<?> type = getSetterType(prop.getName());
try {
// 创建对象
Object newObject = objectFactory.create(type);
// 创建 MetaObject 对象
metaValue = MetaObject.forObject(newObject, metaObject.getObjectFactory(), metaObject.getObjectWrapperFactory(), metaObject.getReflectorFactory());
// <1> 设置当前对象的值
set(prop, newObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ReflectionException(“Cannot set value of property ‘“ + name + “‘ because ‘“ + name + “‘ is null and cannot be instantiated on instance of “ + type.getName() + “. Cause:” + e.toString(), e);
}
return metaValue;
}
1 |
|
// BeanWrapper.java
@Override
public boolean isCollection() {
return false;
}
1 |
|
// BeanWrapper.java
@Override
public void add(Object element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
1 |
|
// MapWrapper.java
// object 变成了 map
private final Map<String, Object> map;
// 属性的操作变成了
map.put(prop.getName(), value);
map.get(prop.getName());
1 |
|
// CollectionWrapper.java
public class CollectionWrapper implements ObjectWrapper {
private final Collection<Object> object;
public CollectionWrapper(MetaObject metaObject, Collection<Object> object) {
this.object = object;
}
@Override
public Object get(PropertyTokenizer prop) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public void set(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public String findProperty(String name, boolean useCamelCaseMapping) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public String[] getGetterNames() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public String[] getSetterNames() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getSetterType(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getGetterType(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean hasSetter(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean hasGetter(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public MetaObject instantiatePropertyValue(String name, PropertyTokenizer prop, ObjectFactory objectFactory) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean isCollection() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void add(Object element) {
object.add(element);
}
@Override
public <E> void addAll(List<E> element) {
object.addAll(element);
}
}
1 |
|
// ObjectWrapperFactory.java
public interface ObjectWrapperFactory {
/**
* 是否包装了指定对象
*
* @param object 指定对象
* @return 是否
*/
boolean hasWrapperFor(Object object);
/**
* 获得指定对象的 ObjectWrapper 对象
*
* @param metaObject MetaObject 对象
* @param object 指定对象
* @return ObjectWrapper 对象
*/
ObjectWrapper getWrapperFor(MetaObject metaObject, Object object);
}
1 |
|
public class DefaultObjectWrapperFactory implements ObjectWrapperFactory {
@Override
public boolean hasWrapperFor(Object object) {
return false;
}
@Override
public ObjectWrapper getWrapperFor(MetaObject metaObject, Object object) {
throw new ReflectionException("The DefaultObjectWrapperFactory should never be called to provide an ObjectWrapper.");
}
}
1 |
|
// MetaObject.java
/**
- 原始 Object 对象
/
private final Object originalObject;
/* - 封装过的 Object 对象
*/
private final ObjectWrapper objectWrapper;
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
private final ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory;
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
private MetaObject(Object object, ObjectFactory objectFactory, ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
this.originalObject = object;
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
this.objectWrapperFactory = objectWrapperFactory;
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
// <1>
if (object instanceof ObjectWrapper) {
this.objectWrapper = (ObjectWrapper) object;
} else if (objectWrapperFactory.hasWrapperFor(object)) { // <2>
// 创建 ObjectWrapper 对象
this.objectWrapper = objectWrapperFactory.getWrapperFor(this, object);
} else if (object instanceof Map) {
// 创建 MapWrapper 对象
this.objectWrapper = new MapWrapper(this, (Map) object);
} else if (object instanceof Collection) {
// 创建 CollectionWrapper 对象
this.objectWrapper = new CollectionWrapper(this, (Collection) object);
} else {
// 创建 BeanWrapper 对象
this.objectWrapper = new BeanWrapper(this, object);
}
}
1 |
|
处,会根据
1 | object |
类型的不同,创建对应的 ObjectWrapper 对象。
- 其中,
<2>处,我们可以看到 ObjectWrapperFactory 的使用,因为默认情况下的 DefaultObjectWrapperFactory 未实现任何逻辑,所以这块逻辑相当于暂时不起作用。如果想要起作用,需要自定义 ObjectWrapperFactory 的实现类。
10.2 forObject
#forObject(Object object, ObjectFactory objectFactory, ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) 静态方法,创建 MetaObject 对象。代码如下:
1 | // MetaObject.java |
- 如果
object为空的情况下,返回SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT。
10.3 metaObjectForProperty
#metaObjectForProperty(String name) 方法,创建指定属性的 MetaObject 对象。代码如下:
1 | // MetaObject.java |
10.4 getValue
#getValue(String name) 方法,获得指定属性的值。代码如下:
1 | // MetaObject.java |
- 大体逻辑上,就是不断对
name分词,递归查找属性,直到<1>处,返回最终的结果。 - 比较特殊的是,在
<2>处,如果属性的值为null时,则直接返回null,因为值就是空的哈。
10.5 setValue
#setValue(String name, Object value) 方法,设置指定属性的指定值。代码如下:
1 | // MetaObject.java |
- 大体逻辑上,就是不断对
name分词,递归查找属性,最终在<1>处,设置对应的值。 - 比较特殊的是,在
<2>处,如果属性的值为null时,调用ObjectWrapper#instantiatePropertyValue(name, prop, objectFactory)方法,创建当前name的prop属性的空对象,然后继续递归。可能有点难理解,胖友可以调试下MetaObjectTest#shouldGetAndSetNestedMapPairUsingArraySyntax()这个单元测试方法。
10.6 isCollection
#isCollection() 方法,判断是否为集合。代码如下:
1 | // MetaObject.java |
- 直接调用
objectWrapper的对应的方法。
11. SystemMetaObject
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.SystemMetaObject ,系统级的 MetaObject 对象,主要提供了 ObjectFactory、ObjectWrapperFactory、空 MetaObject 的单例。代码如下:
1 | // SystemMetaObject.java |
- 核心就是
#forObject(Object object)方法,创建指定对象的 MetaObject 对象。
12. ParamNameUtil
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameUtil ,参数名工具类,获得构造方法、普通方法的参数列表。代码如下:
1 | // ParamNameUtil.java |
13. ParamNameResolver
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameResolver ,参数名解析器。
13.1 构造方法
1 | // ParamNameResolver.java |
- 代码比较简单,胖友看下注释。
13.2 getNamedParams
#getNamedParams(Object[] args) 方法,获得参数名与值的映射。代码如下:
1 | // ParamNameResolver.java |
- 代码比较简单,胖友看下注释。
14. TypeParameterResolver
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolver ,工具类,java.lang.reflect.Type 参数解析器。因为 Type 是相对冷门的知识,我表示也不会,所以推荐先阅读如下任一文章:
- 贾博岩 《我眼中的 Java-Type 体系(1)》
- xujun9411 《java Type 详解》
FROM 西瓜1994 《MyBatis源码分析-2-基础支持层-反射模块-TypeParameterResolver/ObjectFactory》
当存在复杂的继承关系以及泛型定义时, TypeParameterResolver 可以帮助我们解析字段、方法参数或方法返回值的类型。
14.1 暴露方法
TypeParameterResolver 暴露了三个 公用静态方法,分别用于解析 Field 类型、Method 返回类型、方法参数类型。代码如下:
1 | // TypeParameterResolver.java |
- 大体逻辑都类似,最终都会调用
#resolveType(Type type, Type srcType, Class<?> declaringClass)方法,解析类型。详细解析,见 「4.2 resolveType」 。
14.2 resolveType
#resolveType(Type type, Type srcType, Class<?> declaringClass) 方法,解析 type 类型。代码如下:
1 | // TypeParameterResolver.java |
- 根据
type对应不同的 Type 类型,调用不同的方法,进行解析。
14.2.1 resolveParameterizedType
#resolveParameterizedType(ParameterizedType parameterizedType, Type srcType, Class<?> declaringClass) 方法,解析 ParameterizedType 类型。代码如下:
1 | // TypeParameterResolver.java |
【1】处,解析<>中实际类型。【2】处,创建 ParameterizedTypeImpl 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56// TypeParameterResolver.java 内部静态类
/**
* ParameterizedType 实现类
*
* 参数化类型,即泛型。例如:List<T>、Map<K, V>等带有参数化的配置
*/
static class ParameterizedTypeImpl implements ParameterizedType {
// 以 List<T> 举例子
/**
* <> 前面实际类型
*
* 例如:List
*/
private Class<?> rawType;
/**
* 如果这个类型是某个属性所有,则获取这个所有者类型;否则,返回 null
*/
private Type ownerType;
/**
* <> 中实际类型
*
* 例如:T
*/
private Type[] actualTypeArguments;
public ParameterizedTypeImpl(Class<?> rawType, Type ownerType, Type[] actualTypeArguments) {
super();
this.rawType = rawType;
this.ownerType = ownerType;
this.actualTypeArguments = actualTypeArguments;
}
@Override
public Type[] getActualTypeArguments() {
return actualTypeArguments;
}
@Override
public Type getOwnerType() {
return ownerType;
}
@Override
public Type getRawType() {
return rawType;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ParameterizedTypeImpl [rawType=" + rawType + ", ownerType=" + ownerType + ", actualTypeArguments=" + Arrays.toString(actualTypeArguments) + "]";
}
}
14.2.2 resolveWildcardType
#resolveWildcardType(WildcardType wildcardType, Type srcType, Class<?> declaringClass) 方法,解析 WildcardType 类型。代码如下:
1 | // TypeParameterResolver.java |
<1.1>、<1.2>处,解析泛型表达式下界(下限super)和上界( 上限extends)。<2>创建 WildcardTypeImpl 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49// TypeParameterResolver.java 内部静态类
/**
* WildcardType 实现类
*
* 泛型表达式(或者通配符表达式),即 ? extend Number、? super Integer 这样的表达式。
* WildcardType 虽然是 Type 的子接口,但却不是 Java 类型中的一种。
*/
static class WildcardTypeImpl implements WildcardType {
/**
* 泛型表达式下界(下限 super)
*/
private Type[] lowerBounds;
/**
* 泛型表达式上界(上界 extends)
*/
private Type[] upperBounds;
WildcardTypeImpl(Type[] lowerBounds, Type[] upperBounds) {
super();
this.lowerBounds = lowerBounds;
this.upperBounds = upperBounds;
}
@Override
public Type[] getLowerBounds() {
return lowerBounds;
}
@Override
public Type[] getUpperBounds() {
return upperBounds;
}
}
static class GenericArrayTypeImpl implements GenericArrayType {
private Type genericComponentType;
GenericArrayTypeImpl(Type genericComponentType) {
super();
this.genericComponentType = genericComponentType;
}
@Override
public Type getGenericComponentType() {
return genericComponentType;
}
}
14.2.3 resolveGenericArrayType
1 | // TypeParameterResolver.java |
【1】处,解析componentType类型。【2】处,创建 GenericArrayTypeImpl 对象。代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25// TypeParameterResolver.java 内部静态类
/**
* GenericArrayType 实现类
*
* 泛型数组类型,用来描述 ParameterizedType、TypeVariable 类型的数组;即 List<T>[]、T[] 等;
*/
static class GenericArrayTypeImpl implements GenericArrayType {
/**
* 数组元素类型
*/
private Type genericComponentType;
GenericArrayTypeImpl(Type genericComponentType) {
super();
this.genericComponentType = genericComponentType;
}
@Override
public Type getGenericComponentType() {
return genericComponentType;
}
}
14.2.4 resolveTypeVar
TODO 1001 芋艿,暂时看不太懂。暂时无视
想要死磕的胖友,可以看看 《mybatis-TypeParameterResolver 工具类分析》 。
可以通过调试 org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolverTest 这个单元测试类,触发各种情况。
15. ArrayUtil
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ArrayUtil ,数组工具类。代码如下:
1 | // ArrayUtil.java |
16. ExceptionUtil
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil ,异常工具类。代码如下:
1 | // ExceptionUtil.java |
666. 彩蛋
比想象中,长了超级超级超级多的文章。写的都快吐血了,鬼知道我经历了什么!!!
参考和推荐如下文章:
如果胖友看到此处,还是一脸懵逼,还是那句话,多多调试!!!